Introduction to Brain Monitoring During Anesthesia
Brain monitoring during anesthesia is a crucial aspect of patient care, ensuring optimal levels of consciousness and preventing potential brain injury during surgical procedures. Anesthesia can affect brain activity, and real-time monitoring allows anesthesiologists to adjust drug levels, maintain proper sedation, and avoid complications such as awareness during surgery or overdose.
Why is Brain Monitoring During Anesthesia Important?
The primary goal of brain monitoring during anesthesia is to safeguard the patient’s neurological functions. When patients undergo surgery, it's essential to strike a balance between providing enough anesthesia to prevent pain and awareness while avoiding over-sedation, which could lead to brain damage or delayed recovery. Brain monitoring devices, such as bispectral index (BIS) monitors and electroencephalography (EEG), help anesthesiologists measure the brain’s electrical activity and fine-tune anesthesia dosages accordingly.
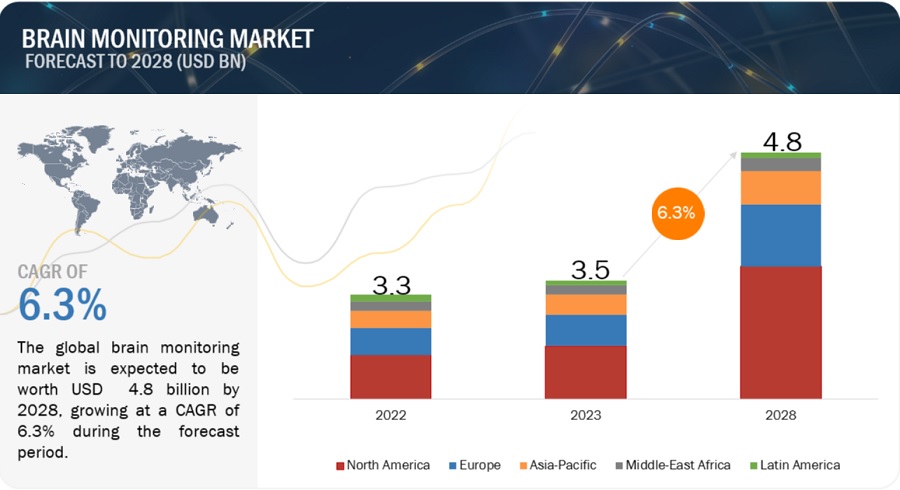
Technological Advancements in Brain Monitoring
With the advent of advanced monitoring technologies, such as depth of anesthesia (DoA) monitoring systems, anesthesiologists can ensure patient safety more effectively. These systems use complex algorithms to provide a real-time assessment of the patient’s brain activity, helping clinicians adjust anesthesia levels with precision. This reduces the risk of intraoperative awareness and promotes faster post-operative recovery.
Benefits of Brain Monitoring During Anesthesia
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Continuous monitoring of brain activity prevents potential complications related to over- or under-dosing of anesthetic drugs.
- Improved Postoperative Recovery: Optimizing anesthesia levels during surgery reduces postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction, especially in elderly patients.
- Reduced Risk of Awareness: With real-time data, anesthesiologists can minimize the risk of patients becoming conscious during surgery, a rare but traumatic experience.
Future Trends in Brain Monitoring During Anesthesia
As technology advances, brain monitoring during anesthesia is expected to become even more precise. Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) systems may further enhance the ability to predict and prevent anesthesia-related complications. The adoption of non-invasive monitoring methods will also contribute to wider usage in various clinical settings.
Conclusion
In summary, brain monitoring during anesthesia is an essential practice for ensuring patient safety and improving surgical outcomes. With advanced technologies and continuous innovation, this field will play an increasingly vital role in modern anesthesiology, reducing risks and promoting faster recovery times for patients undergoing surgery.
Content Source:
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/PressReleases/brain-monitoring-devices.asp
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/brain-monitoring-devices-market-909.html





