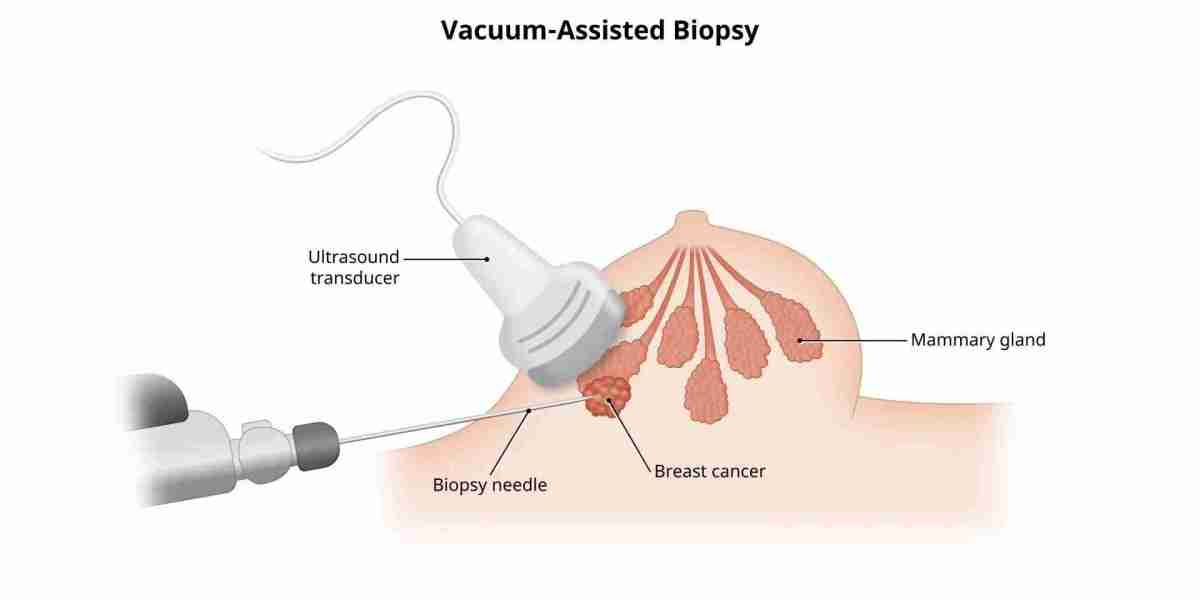
Biopsy procedures are essential diagnostic tools that play a pivotal role in detecting and understanding various medical conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore every step of the biopsy process—from preparation to post-procedure care—to help you better understand how these procedures are performed and why they are so important.
- • Overview of biopsy procedures as a diagnostic tool
- • Importance of understanding the process
- • What readers can expect to learn from this manual
In modern healthcare, accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment planning. For many conditions, a biopsy for diagnostic purposes (خزعة لأغراض التشخيص) is the most reliable way to obtain the necessary tissue samples for analysis.
- • Emphasis on accuracy in diagnosis
- • Role of tissue sampling in confirming diseases
- • Assurance of reliable results through the procedure
This manual is designed for patients, caregivers, and anyone interested in learning more about the step-by-step process of biopsy procedures. Whether you are preparing for your own procedure or simply want to gain a better understanding of how biopsies contribute to diagnostic accuracy, this guide will offer detailed insights into each phase of the process.
- • Target audience: patients, caregivers, and the curious
- • Clarification of the manual’s objective
- • A promise of in-depth, easy-to-understand explanations
What Is a Biopsy?
Defining the Biopsy Process
A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue is removed from the body for diagnostic examination. This tissue is then analyzed in a laboratory to help diagnose diseases, including cancer, infections, and inflammatory conditions.
- • Definition of biopsy
- • Role in diagnosing diseases
- • Laboratory analysis of tissue samples
Biopsies can be performed on nearly any part of the body and are chosen based on the location and nature of the suspected condition. The process is typically minimally invasive, making it a safe and effective diagnostic tool.
- • Versatility of biopsy locations
- • Minimally invasive nature of the procedure
- • Emphasis on safety and effectiveness
Why Biopsies Are Essential
The main goal of a biopsy is to provide a clear picture of the underlying pathology that may not be apparent through imaging tests alone. By examining the tissue under a microscope, pathologists can detect cellular changes and abnormalities, enabling them to make a definitive diagnosis.
- • Importance of microscopic examination
- • Detecting cellular abnormalities
- • Complementing imaging tests for accurate diagnosis
Biopsies help clinicians determine the best course of treatment and are particularly crucial in diagnosing cancers, where early detection can significantly improve outcomes.
- • Contribution to early diagnosis
- • Role in treatment planning
- • Impact on patient prognosis
Indications and Purpose
When Is a Biopsy Recommended?
Biopsies are recommended when imaging tests or physical examinations reveal abnormalities that require further investigation. Conditions such as suspicious lumps, unexplained inflammation, or lesions often necessitate a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
- • Indications include abnormal imaging findings
- • Use in confirming suspicious lesions or inflammation
- • Essential step in the diagnostic workflow
The Role of Biopsy in Treatment Planning
The information gathered from a biopsy can directly influence treatment decisions. By understanding the nature of the tissue abnormality, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment strategies, whether that involves surgery, medication, or other therapeutic interventions.
- • Influence on clinical decision-making
- • Tailoring of treatment strategies
- • Ensuring targeted and effective care
Step-by-Step Process Overview
Understanding the biopsy process can alleviate anxiety and help patients know what to expect. This section breaks down the procedure into clear, manageable steps.
Step 1: Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the biopsy, patients are given detailed instructions on how to prepare. This may include fasting for a few hours, avoiding certain medications, or ensuring that any necessary pre-procedure tests are completed.
- • Importance of following pre-procedure instructions
- • Steps to ensure patient readiness
- • Overview of necessary preparations
Step 2: Consultation and Planning
During the consultation, your healthcare provider explains the procedure, discusses the potential risks, and answers any questions you may have. This step is crucial for ensuring that you are comfortable and fully informed.
- • Detailed discussion of the procedure
- • Addressing patient concerns and questions
- • Establishing trust and clarity between patient and provider
Step 3: Anesthesia and Comfort Measures
Depending on the type of biopsy, local anesthesia is often administered to numb the area. In some cases, sedation may also be used to ensure patient comfort throughout the procedure.
- • Use of local anesthesia to reduce pain
- • Options for sedation for added comfort
- • Emphasis on patient safety and comfort during the procedure
Step 4: Tissue Sample Collection
The actual biopsy involves the careful removal of a small tissue sample using specialized instruments. This step is performed with precision to ensure that an adequate sample is obtained while minimizing discomfort.
- • Explanation of tissue sample collection
- • Use of specialized instruments
- • Emphasis on precision and minimal invasiveness
Step 5: Post-Procedure Observation
After the tissue is collected, patients are usually monitored for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications. Instructions on how to care for the biopsy site are provided before you leave.
- • Monitoring for immediate post-procedure complications
- • Clear instructions for site care
- • Importance of follow-up and observation
Step 6: Laboratory Analysis
The collected tissue is sent to a laboratory, where pathologists examine it under a microscope. This analysis is key to confirming a diagnosis and determining the next steps in treatment.
- • Process of sending tissue for analysis
- • Role of pathologists in examining the sample
- • How laboratory results contribute to diagnosis
Step 7: Follow-Up Consultation
Once the laboratory results are available, a follow-up consultation is scheduled. During this appointment, the results are discussed, and treatment plans are developed based on the findings.
- • Importance of follow-up consultations
- • Discussion of laboratory results
- • Formulating a treatment plan based on the diagnosis
Preparation for the Biopsy Procedure
Understanding the Instructions
Proper preparation is key to ensuring a smooth biopsy procedure. Your healthcare provider will offer a set of instructions that may include dietary restrictions, medication adjustments, and tips for a stress-free experience.
- • Emphasis on following pre-procedure guidelines
- • Overview of common preparation instructions
- • Tips to reduce stress and anxiety before the procedure
What to Bring on the Day of the Procedure
On the day of the biopsy, it is important to bring any necessary documents, identification, and a list of current medications. Being well-prepared can help the process go smoothly and efficiently.
- • Checklist of items to bring
- • Importance of carrying medication lists
- • Ensuring that all pre-procedure paperwork is complete
Communicating with Your Healthcare Team
Effective communication with your healthcare team is crucial. Be sure to inform them of any allergies, medical conditions, or concerns you might have before the procedure.
- • Encouragement to ask questions
- • Importance of sharing medical history
- • Building a trusting relationship with the care team
The Biopsy Procedure in Detail
The Setting and Environment
Biopsy procedures are usually performed in a controlled medical environment, such as a hospital or outpatient center. The setting is designed to ensure safety and comfort for all patients.
- • Description of typical biopsy settings
- • Emphasis on a sterile and controlled environment
- • Patient comfort as a priority
The Role of Imaging Guidance
In many cases, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT, or MRI are used to guide the biopsy needle to the exact location of the abnormal tissue. This imaging guidance enhances the precision of the procedure.
- • Use of advanced imaging for precision
- • How imaging guidance improves sample accuracy
- • Benefits of combining imaging with biopsy techniques
How the Procedure Is Performed
During the procedure, a small incision may be made if necessary, and a needle or specialized instrument is used to extract the tissue sample. The process is quick and carefully monitored by medical professionals.
- • Step-by-step breakdown of tissue extraction
- • Role of specialized instruments
- • Emphasis on speed and monitoring during the procedure
Safety Measures and Patient Comfort
Throughout the procedure, various safety measures are in place to minimize the risk of infection and ensure patient comfort. Sterilization of equipment, proper use of anesthesia, and close monitoring are all part of the process.
- • Overview of safety protocols
- • Importance of sterilization and infection control
- • Measures to ensure minimal discomfort
Post-Procedure Care
Immediate Aftercare Instructions
After a biopsy, patients are given detailed aftercare instructions. These typically include how to care for the biopsy site, signs of infection to watch for, and guidelines on physical activity.
- • Detailed aftercare guidelines
- • Instructions for wound care
- • Signs and symptoms that require attention
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Mild discomfort or pain is common after a biopsy, and your healthcare team will likely recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or other methods to manage it. It is important to follow these recommendations closely.
- • Options for managing post-procedure pain
- • Advice on medication and rest
- • Importance of monitoring discomfort levels
Recognizing Signs of Complications
While biopsy procedures are generally safe, complications can occur. Patients should be aware of symptoms such as excessive bleeding, severe pain, or signs of infection, and contact their healthcare provider if these occur.
- • List of potential post-procedure complications
- • Guidance on when to seek medical help
- • Importance of vigilance in the recovery phase
Scheduling Follow-Up Appointments
A follow-up appointment is typically scheduled to review the biopsy results and ensure that the biopsy site is healing properly. This appointment is critical for addressing any lingering issues and planning next steps.
- • Importance of follow-up care
- • What to expect during follow-up appointments
- • How follow-up ensures long-term healing
Risks, Benefits, and Common Concerns
Understanding the Benefits
Biopsies offer significant benefits by providing definitive diagnostic information that can guide effective treatment plans. They are essential for confirming or ruling out serious conditions.
- • Role in accurate diagnosis
- • Contribution to effective treatment planning
- • How results can impact overall health management
Addressing the Risks
Like any medical procedure, biopsies carry some risks, including bleeding, infection, or minor discomfort. However, these risks are minimized through strict adherence to safety protocols and modern medical practices.
- • Overview of potential risks
- • Explanation of safety measures in place
- • Emphasis on risk minimization through modern techniques
Patient Concerns and Reassurance
Patients often have concerns about the invasiveness and potential pain associated with biopsies. It is important to understand that most biopsies are minimally invasive and designed with patient comfort in mind.
- • Addressing common patient fears
- • Reassurance about the minimally invasive nature
- • Importance of clear communication with healthcare providers
In this section, we also highlight that a biopsy for diagnostic purposes can be a critical tool in identifying conditions early, ensuring that patients receive timely and appropriate care.
- • Reinforcement of the importance of early diagnosis
- • Assurance of the procedure's diagnostic value
- • Emphasis on the procedure’s role in improving patient outcomes
Common Uses and Applications
Diagnosing Cancer
One of the most critical applications of biopsy procedures is in the diagnosis of cancer. By analyzing tissue samples, doctors can determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant, which is crucial for planning treatment.
- • Importance of biopsy in cancer diagnosis
- • Differentiating between benign and malignant tumors
- • Impact on treatment strategy
Investigating Inflammatory Conditions
Biopsies are also used to diagnose inflammatory conditions such as hepatitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other autoimmune disorders. The tissue analysis can reveal the extent of inflammation and guide treatment decisions.
- • Role in diagnosing inflammatory diseases
- • How tissue analysis helps in determining inflammation
- • Contribution to tailored treatment approaches
Evaluating Unexplained Symptoms
For patients experiencing unexplained symptoms or persistent issues, a biopsy may be recommended to rule out or confirm underlying conditions that are not apparent through other diagnostic methods.
- • Use in evaluating ambiguous or persistent symptoms
- • Importance of ruling out hidden conditions
- • Benefits of confirming a diagnosis through tissue analysis
Research and Clinical Trials
Biopsies are not only used for individual patient care but also play a significant role in clinical research. Tissue samples help researchers understand disease mechanisms and develop new treatments.
- • Contribution to medical research
- • Role in advancing clinical trials
- • Importance in understanding disease progression
Future Developments in Biopsy Procedures
Technological Advancements
Advances in technology are continuously improving the precision and safety of biopsy procedures. Innovations such as robotic assistance and enhanced imaging techniques are paving the way for even less invasive and more accurate biopsies in the future.
- • Overview of emerging technological innovations
- • Role of robotics and improved imaging
- • Future potential for enhanced safety and precision
Personalized Medicine
The future of diagnostic biopsies lies in personalized medicine. As our understanding of genetic and molecular markers grows, biopsy samples will play a crucial role in tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles.
- • Role of biopsies in personalized treatment
- • Integration of genetic and molecular analysis
- • Benefits of customized therapeutic approaches
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in the analysis of biopsy samples promises to revolutionize diagnostic accuracy. AI algorithms can help pathologists detect subtle abnormalities that may be missed by the human eye, leading to quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
- • Potential of AI in tissue analysis
- • Improved detection of subtle abnormalities
- • Impact on diagnostic turnaround times
Conclusion
Biopsy procedures are a cornerstone of modern diagnostic medicine, providing critical information that guides treatment decisions and improves patient outcomes. This manual has provided a detailed, step-by-step overview of the biopsy process—from preparation and procedure to post-care and follow-up.
- • Recap of the step-by-step biopsy process
- • Emphasis on the role of biopsies in diagnosis
- • Final thoughts on the importance of accurate, safe procedures
By understanding the process thoroughly, patients and caregivers can approach biopsies with greater confidence and clarity. Whether it is diagnosing cancer, investigating inflammatory conditions, or contributing to groundbreaking research, a well-executed biopsy is invaluable. Remember, if you have concerns or need more detailed information, always consult your healthcare provider for guidance tailored to your situation. Additionally, the value of a biopsy for diagnostic purposes in guiding treatment and improving outcomes cannot be overstated.
- • Importance of being well-informed about biopsy procedures
- • Encouragement to communicate openly with healthcare providers
- • Final reassurance on the safety and efficacy of the procedure
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a biopsy for diagnostic purposes?
A biopsy for diagnostic purposes is a procedure where a small sample of tissue is removed from the body and analyzed in a laboratory. This helps in accurately diagnosing conditions such as cancer, infections, or inflammatory diseases.
- • Definition and purpose of the biopsy
- • Emphasis on tissue analysis for diagnosis
- • Overview of common conditions diagnosed
How should I prepare for a biopsy?
Preparation for a biopsy typically involves following your healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include fasting, avoiding certain medications, and ensuring you bring any required documents on the day of the procedure.
- • Importance of following preparation instructions
- • Common guidelines to expect
- • Tips for a smooth pre-procedure experience
What are the risks associated with a biopsy?
While biopsies are generally safe, there are some risks such as bleeding, infection, and mild discomfort. However, these risks are minimized by strict adherence to safety protocols and are monitored closely by healthcare professionals.
- • Overview of potential risks
- • Explanation of safety measures in place
- • Reassurance about the overall safety of the procedure
How long does it take to get biopsy results?
The time it takes to receive biopsy results can vary, but it generally takes a few days to a week. The tissue sample is processed and examined by a pathologist, who then provides a detailed report to your healthcare provider.
- • Typical turnaround time for results
- • Explanation of the laboratory process
- • Importance of follow-up consultations for result discussions
By addressing these common questions and explaining the entire process in detail, this manual aims to demystify the procedure and provide you with a solid understanding of how biopsies play an integral role in modern diagnostics. Embracing the information provided can help reduce anxiety and empower you to make informed decisions about your healthcare journey.
- • Final reassurance and summary of key points
- • Encouragement to ask further questions if needed
- • Emphasis on the critical role of biopsies in accurate diagnosis