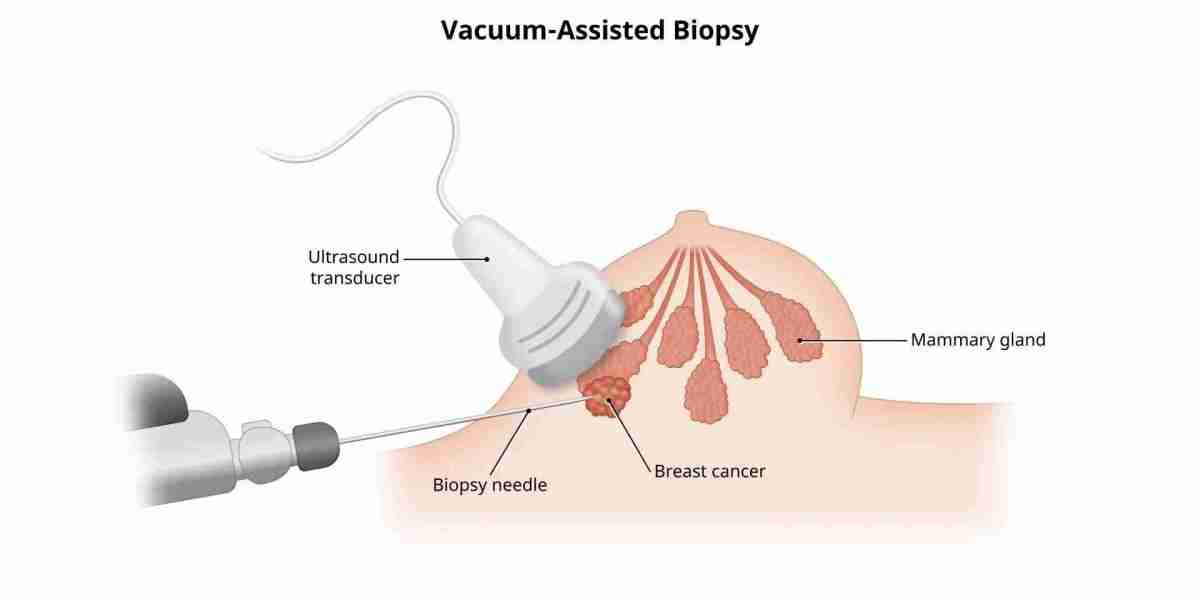
When it comes to diagnosing medical conditions accurately, a biopsy for diagnostic purposes (خزعة لأغراض التشخيص) is one of the most reliable methods available. This procedure involves taking a small sample of tissue from the body to examine it under a microscope, helping healthcare professionals identify diseases, infections, or abnormalities. Whether you’re preparing for a biopsy or simply want to understand the process, this guide will provide you with all the essential information you need.
What Is a Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes?
Definition and Overview
A biopsy for diagnostic purposes is a medical procedure where a small sample of tissue or cells is removed from the body for laboratory analysis. It is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as cancer, infections, or inflammatory diseases.
Why Is It Important?
Biopsies play a critical role in confirming diagnoses, especially when other tests like imaging or blood work are inconclusive. They provide detailed insights into the nature of the tissue, helping doctors plan effective treatment strategies.
Common Types of Biopsies
There are several types of biopsies, including needle biopsies, surgical biopsies, and skin biopsies. The type chosen depends on the location and nature of the suspected condition.
How Is a Biopsy Performed?
Step-by-Step Procedure
The biopsy process typically involves numbing the area with local anesthesia, followed by the removal of a tissue sample using specialized tools. The procedure is usually quick and minimally invasive.
Tools and Techniques Used
Different tools are used depending on the type of biopsy. For example, fine-needle aspiration uses a thin needle, while core needle biopsies use a larger needle to extract a tissue sample.
What Happens After the Sample Is Taken?
The tissue sample is sent to a laboratory, where it is examined by a pathologist. Results are usually available within a few days to a week.
Why Is a Biopsy Recommended?
Identifying Cancer and Other Diseases
A biopsy is often recommended when cancer is suspected. It helps determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant and provides information about its stage and grade.
Confirming Infections or Inflammatory Conditions
Infections, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory conditions can also be diagnosed through a biopsy. It helps identify the specific cause of the issue.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
In some cases, biopsies are used to monitor how well a treatment is working, such as checking for cancer recurrence after therapy.
Preparing for a Biopsy
Consultation and Medical History
Before the procedure, your doctor will review your medical history and explain the process. This is also an opportunity to ask questions and address any concerns.
Pre-Procedure Instructions
You may be asked to avoid certain medications, fasting, or other preparations depending on the type of biopsy. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
What to Bring on the Day of the Procedure
Bring any necessary documents, such as your ID and insurance information. Wear comfortable clothing and arrange for someone to drive you home if needed.
What to Expect During the Procedure
Pain Management and Anesthesia
Most biopsies are performed under local anesthesia, so you’ll be awake but won’t feel pain. In some cases, sedation or general anesthesia may be used.
Duration of the Procedure
The procedure usually takes between 15 minutes to an hour, depending on the type and location of the biopsy.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects include mild pain, bruising, or swelling at the biopsy site. These usually resolve within a few days.
After the Biopsy: Recovery and Results
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
You may need to rest for a short period after the procedure. Keep the biopsy site clean and follow any specific care instructions provided by your doctor.
Understanding Your Biopsy Results
Your doctor will discuss the results with you, explaining what they mean and the next steps. If abnormalities are found, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
Follow-Up Appointments
Depending on the results, you may need follow-up appointments to monitor your condition or begin treatment.
Risks and Benefits of a Biopsy
Potential Risks
While biopsies are generally safe, there are some risks, such as infection, bleeding, or damage to nearby tissues. These are rare and usually minor.
Key Benefits
The primary benefit of a biopsy is its ability to provide a definitive diagnosis, which is crucial for effective treatment planning.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Your doctor will help you understand the risks and benefits specific to your situation, ensuring you make an informed decision.
Common Myths About Biopsies
Myth 1: Biopsies Are Always Painful
Most biopsies are performed under anesthesia, so pain is minimal. Any discomfort is usually short-lived.
Myth 2: Biopsies Spread Cancer
There is no evidence to suggest that biopsies cause cancer to spread. They are a safe and standard diagnostic tool.
Myth 3: Biopsies Are Only for Cancer
While biopsies are commonly used to diagnose cancer, they are also used for many other conditions, including infections and autoimmune diseases.
FAQs About Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes
1. How long does it take to get biopsy results?
Results typically take a few days to a week, depending on the complexity of the analysis required.
2. Is a biopsy safe?
Yes, biopsies are generally safe when performed by trained professionals. Risks are minimal and rare.
3. Can I eat or drink before a biopsy?
This depends on the type of biopsy. Your doctor will provide specific instructions regarding fasting or dietary restrictions.
4. What if my biopsy results are abnormal?
Abnormal results may indicate a medical condition that requires further testing or treatment. Your doctor will guide you through the next steps.
Conclusion
A biopsy for diagnostic purposes is a vital tool in modern medicine, offering precise insights into various medical conditions. Whether you’re facing a potential diagnosis or simply want to understand the process, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of what to expect. By being informed and prepared, you can approach the procedure with confidence and clarity.