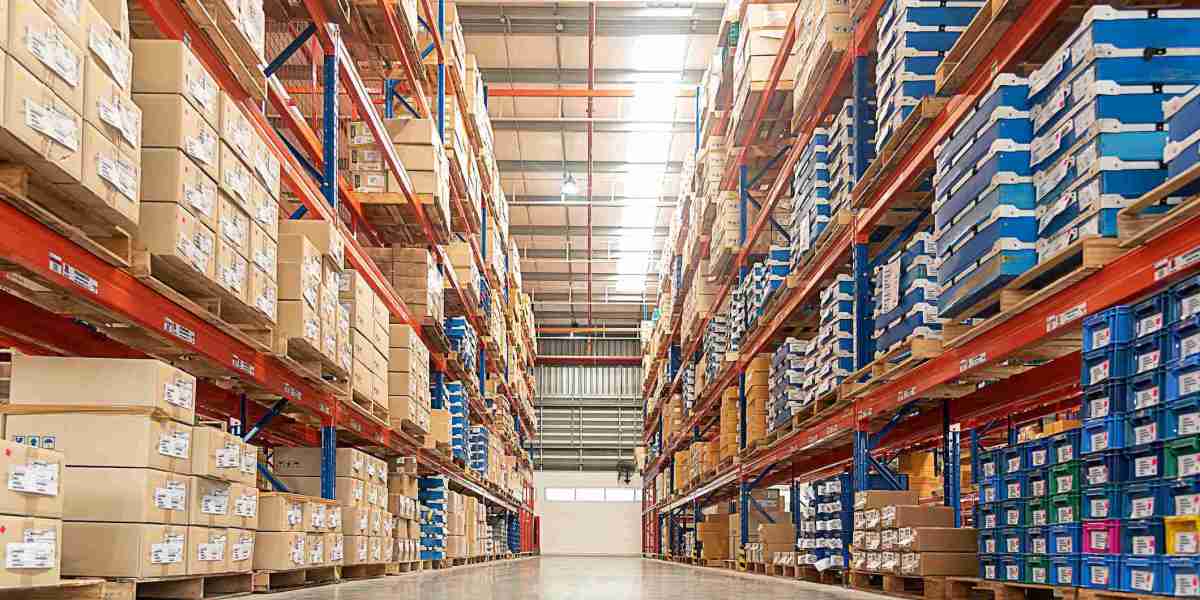
Warehouse Solutions refer to technologies, strategies, and systems designed to optimize storage, inventory management, and order fulfillment in warehouses. As supply chains become more complex, businesses are adopting automated, data-driven, and scalable solutions to enhance warehouse operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
What Are Warehouse Solutions?
Warehouse solutions include a range of technologies and processes that help businesses streamline inventory management, optimize space utilization, and improve order accuracy. These solutions reduce manual labor, improve workflow efficiency, and ensure faster order processing.
Key Features of Warehouse Solutions:
✅ Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) for efficiency.
✅ Real-time inventory tracking to prevent stockouts and overstocking.
✅ AI-driven demand forecasting for accurate inventory planning.
✅ Order fulfillment optimization to speed up deliveries.
✅ Integration with logistics and e-commerce platforms for seamless operations.
Types of Warehouse Solutions
1. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is software that helps businesses track inventory, optimize picking and packing, and manage warehouse operations.
- Provides real-time inventory visibility.
- Reduces errors in order fulfillment.
- Improves warehouse space utilization.
- Example: SAP EWM, Manhattan Associates, Oracle WMS.
2. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS use robots, conveyors, and cranes to store and retrieve inventory with minimal human intervention.
- Reduces labor costs and increases efficiency.
- Improves accuracy and space utilization.
- Example: Amazon’s robotic fulfillment centers, AutoStore systems.
3. Smart Inventory Tracking & RFID Technology
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode systems help track inventory in real time.
- Enhances inventory accuracy and reduces theft.
- Speeds up stock movement tracking.
- Example: Walmart’s RFID-enabled supply chain.
4. Pick-to-Light & Voice-Picking Technology
These systems guide warehouse workers to quickly and accurately pick products.
- Reduces human error in order fulfillment.
- Improves productivity and efficiency.
- Example: Zebra Technologies’ voice-directed picking.
5. Robotics & AI-Powered Warehouses
Robots and AI systems help automate picking, sorting, and packing processes.
- Increases warehouse speed and reduces errors.
- Reduces dependency on human labor.
- Example: Boston Dynamics’ warehouse robots, Kiva robots by Amazon.
6. Cold Storage Solutions
For industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, temperature-controlled storage is essential.
- Maintains strict temperature and humidity conditions.
- Prevents spoilage and product degradation.
- Example: Thermo King cold storage systems.
7. Sustainable & Energy-Efficient Warehouses
Businesses are adopting green warehouse solutions to reduce costs and environmental impact.
- Use of solar power, LED lighting, and energy-efficient equipment.
- Eco-friendly packaging and waste management.
- Example: Tesla’s energy-efficient Gigafactories.
8. Cloud-Based Warehouse Solutions
Cloud platforms allow businesses to manage inventory, fulfillment, and logistics remotely.
- Provides real-time data access and analytics.
- Integrates with ERP, e-commerce, and logistics systems.
- Example: Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Supply Chain.
Benefits of Warehouse Solutions
1. Improved Inventory Accuracy
- Reduces errors and prevents overstocking/stockouts.
- Enhances real-time stock visibility.
2. Faster Order Fulfillment
- Optimized picking and packing processes for faster deliveries.
- Increases customer satisfaction and retention.
3. Cost Savings & Labor Efficiency
- Reduces manual work with automation.
- Lowers operational costs and human errors.
4. Enhanced Warehouse Space Utilization
- Optimized layouts and vertical storage solutions.
- Increases storage capacity without expanding facilities.
5. Greater Supply Chain Transparency
- Real-time tracking ensures better demand forecasting.
- Reduces waste, delays, and inefficiencies.
Challenges in Implementing Warehouse Solutions
1. High Initial Investment
- Automation and smart warehouse systems require significant upfront costs.
- Solution: Gradual implementation and phased upgrades.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
- Legacy systems may not be compatible with modern WMS solutions.
- Solution: Use cloud-based and modular platforms.
3. Skilled Workforce Shortage
- Need for trained personnel to operate automated systems.
- Solution: Employee training programs and AI-driven assistance.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
- Digital warehouse solutions are vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Solution: Use secure cloud systems and advanced cybersecurity protocols.
Future Trends in Warehouse Solutions
1. AI & Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
- AI-driven analytics help in demand forecasting and warehouse optimization.
- Reduces waste and improves supply chain agility.
2. Drone Technology for Inventory Audits
- Drones perform real-time inventory checks and tracking.
- Reduces manual labor and speeds up audits.
3. Hyperlocal & Urban Warehousing
- Small, strategically placed warehouses for faster last-mile delivery.
- Supports same-day and next-day delivery models.
4. Blockchain for Secure Supply Chain Management
- Ensures transparent, tamper-proof tracking of goods.
- Reduces fraud and enhances trust.
5. 3D Printing for On-Demand Warehousing
- Warehouses will store digital blueprints instead of physical products.
- Products are manufactured on demand using 3D printing.
Conclusion
Warehouse solutions are transforming modern logistics, enabling businesses to achieve faster, more accurate, and cost-effective supply chain operations. With advancements in automation