Introduction
In an era where accuracy and efficiency define success, Precision Manufacturing is transforming industries by delivering high-quality, meticulously crafted components. With advancements in automation, CNC machining, AI, and IoT-driven technologies, manufacturers can achieve greater consistency, reduce costs, and optimize production processes.
What is Precision Manufacturing?
Precision manufacturing is a highly specialized production method that ensures each component meets strict tolerances and exact specifications. By leveraging automated machinery, 3D printing, and robotics, this approach enhances product quality while minimizing waste and inefficiencies.
Key Benefits
- Superior Accuracy – Ensures precise component production down to the micron level.
- Automation & AI Integration – Reduces manual errors and enhances efficiency.
- Cost Optimization – Lowers production costs through material efficiency.
- Compliance with Industry Standards – Guarantees safety and performance regulations are met.
- Sustainable Manufacturing – Incorporates eco-friendly and energy-efficient processes.
Technologies Shaping Precision Manufacturing
1. AI & Machine Learning for Smart Manufacturing
AI-powered analytics enhance defect detection, workflow automation, and predictive maintenance, resulting in improved operational efficiency.
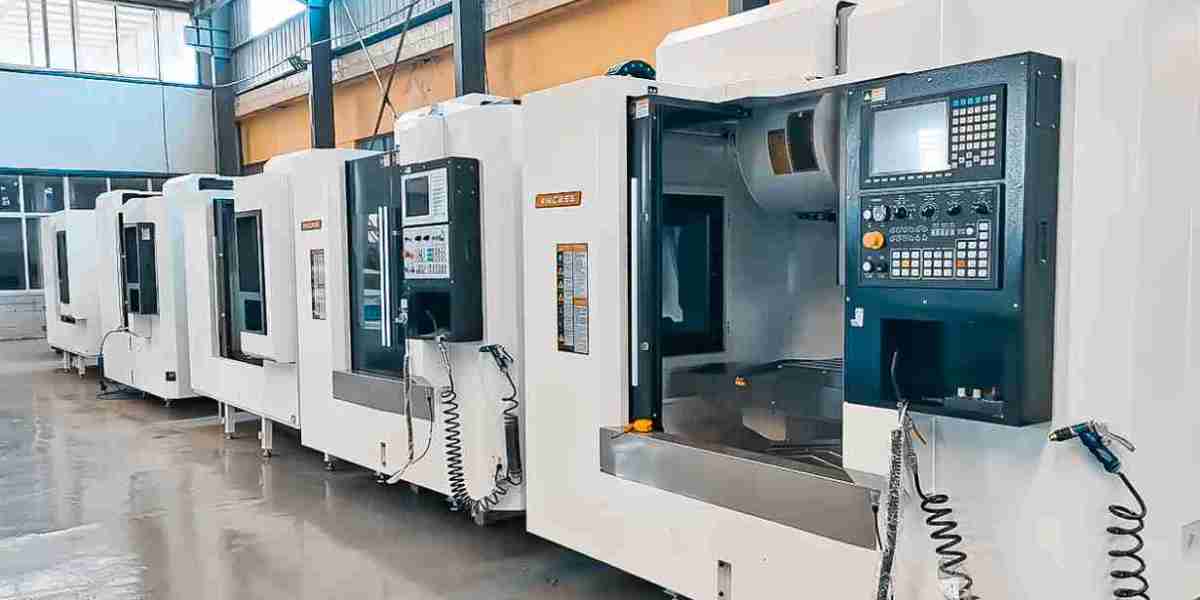
2. CNC Machining for Ultra-Precise Components
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining enables fast, repeatable, and highly accurate fabrication, crucial for industries that demand high precision.
3. 3D Printing & Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing allows for custom, lightweight, and complex parts, accelerating prototyping and reducing material waste.
4. IoT-Enabled Factory Automation
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects factory machinery to monitor production in real time, optimize processes, and improve decision-making.
5. Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology
Utilizing composites, high-performance alloys, and nanotechnology, manufacturers enhance durability, strength, and efficiency in product design.
Industries That Rely on Precision Manufacturing
Aerospace & Defense
Precision manufacturing ensures aircraft components, defense systems, and space technology meet the highest performance and safety standards.
Healthcare & Medical Devices
From biomedical implants to precision surgical instruments, Precision Manufacturing is at the core of medical innovation.
Automotive & Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Precision engineering enhances battery technology, high-efficiency engines, and vehicle safety systems, pushing forward the evolution of transportation.
Electronics & Semiconductor Industry
With growing demand for miniaturized electronics and high-performance computing, precision manufacturing ensures flawless microchip and circuit board production.
Future Trends in Precision Manufacturing
1. Digital Twin Technology for Smart Production
Digital twins allow manufacturers to simulate, analyze, and optimize production workflows, reducing defects and increasing efficiency.
2. AI & Quantum Computing for Next-Level Manufacturing
AI-driven systems and quantum computing will revolutionize material science, predictive analytics, and process automation, shaping the future of industrial production.
3. Human-Robot Collaboration for Enhanced Productivity
Collaborative robots (cobots) will enhance factory automation, improve precision, and boost workplace safety.
Conclusion
As technology advances, Precision Manufacturing continues to lead industries toward greater efficiency, sustainability, and innovation. Companies that invest in these cutting-edge techniques will stay ahead of the competition and define the future of industrial production.