Introduction
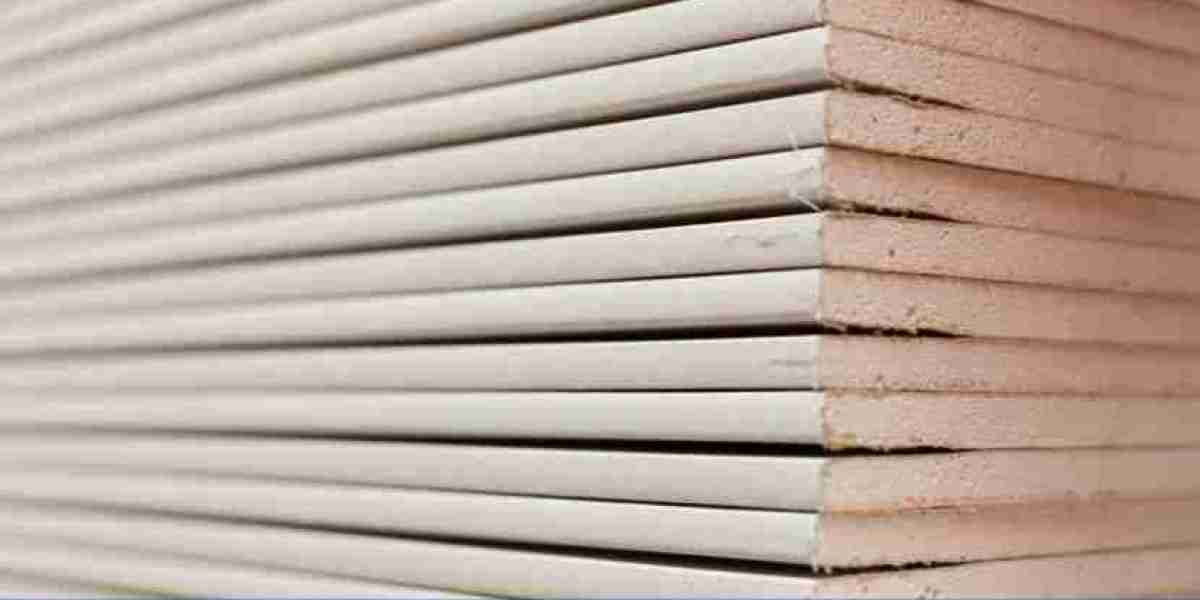
The Gypsum Board Manufacturing Plant Project is focused on producing gypsum boards, which are commonly used in the construction industry for interior wall and ceiling applications. Gypsum board, also known as drywall or plasterboard, has a wide range of benefits, including being lightweight, fire-resistant, soundproof, and easy to install. This Gypsum Board Manufacturing Plant Project Report will outline the necessary steps for setting up a gypsum board manufacturing plant, including market analysis, raw material sourcing, production process, financial projections, and plant design considerations. The growth of the construction and real estate industry, along with the demand for sustainable and cost-effective building materials, makes this a viable investment opportunity.
Market Overview and Demand
The demand for gypsum boards has been steadily increasing due to the rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and the growing construction industry. Gypsum board is widely used for partition walls, ceilings, and as a base for wall coverings in both residential and commercial buildings. The market is driven by several factors:
- Construction Industry Growth: With increasing investments in residential and commercial construction, the demand for gypsum board as an essential building material continues to rise.
- Renovation and Retrofitting: As old buildings are renovated or refurbished, the use of gypsum boards in modernizing interiors is becoming more common.
- Fire Resistance: Gypsum board’s fire-resistant properties make it a preferred choice for both safety and regulatory compliance in building codes.
- Energy Efficiency: The thermal insulation properties of gypsum board contribute to energy savings, making it ideal for modern, energy-efficient buildings.
The growing construction market in developing countries, combined with the increasing demand for eco-friendly and cost-effective building materials, is expected to further drive the demand for gypsum boards.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Raw Materials and Supplies
The primary raw material used in the production of gypsum board is gypsum. Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral that is found naturally in sedimentary rock deposits. In addition to gypsum, other materials are used in the production process to improve the board's strength, fire resistance, and moisture resistance. The essential raw materials for gypsum board production include:
- Gypsum: The main raw material that provides the essential properties of the board. It is usually mined in the form of natural gypsum or obtained as synthetic gypsum from flue gas desulfurization.
- Papers: Recycled paper or new paper is used for the front and back liners of the gypsum board. The paper gives the board strength, enhances durability, and provides an easy surface for painting or finishing.
- Additives and Fillers: Various chemical additives are used to improve the properties of gypsum board, such as binders, retarders, and foaming agents that help enhance fire resistance, water resistance, and strength.
- Water: Water is essential in the gypsum board manufacturing process, used to mix with gypsum to form a paste that is spread between layers of paper.
- Vermiculite or Perlite (optional): For specific products, materials like vermiculite or perlite can be added to the gypsum board for additional fire resistance and thermal insulation.
Sourcing high-quality raw materials is crucial for ensuring the quality and consistency of the gypsum boards produced. Establishing reliable suppliers for gypsum, paper, and other additives will be key to ensuring the smooth operation of the plant.
Manufacturing Process
The production of gypsum board involves several steps, including the preparation of raw materials, forming the boards, and curing the finished products. Below are the steps involved in the manufacturing process:
Raw Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves preparing the raw materials. Natural gypsum or synthetic gypsum is crushed and ground into a fine powder. The gypsum powder is then mixed with water to create a slurry. Additives and fillers are also mixed into the slurry to enhance properties such as fire resistance, strength, and moisture resistance.
Forming the Board
The gypsum slurry is poured onto a continuous conveyor belt, which carries it through a series of rollers that spread it evenly between two sheets of paper. These sheets of paper serve as the liner for the board. The slurry is spread into the desired thickness and length to form the gypsum board.
Setting and Curing
Once the gypsum slurry is formed into the desired shape, the board passes through a drying process. This stage, called curing, involves heating the boards in large kilns to harden the gypsum mixture and remove excess moisture. The boards are allowed to cool and harden, which gives them their characteristic strength and durability. The time and temperature during the curing process must be controlled to ensure consistent quality.
Cutting and Finishing
Once the gypsum board has been cured, it is cut to the required size and shape using automated cutting machines. The edges of the boards may be finished, depending on the desired product specifications. Special boards, such as moisture-resistant or fire-resistant gypsum boards, may undergo additional processing during this stage.
Packaging and Storage
After the boards are cut and finished, they are packaged for distribution. Packaging materials such as plastic wrapping or shrink wrap are used to protect the boards during transportation. The packaged boards are then stored in a warehouse until they are ready to be shipped to customers.
Plant Design and Layout
The design and layout of the gypsum board manufacturing plant should prioritize efficiency, safety, and high-quality production. The key areas in the plant design include:
- Raw Material Storage: A section dedicated to the storage of gypsum, paper, and other raw materials. Proper storage is critical to maintain the quality of the materials, especially paper, which should be stored in a dry environment to prevent damage.
- Mixing Area: The gypsum slurry is prepared and mixed in this area. This section must include proper equipment for accurate mixing and precise measurement of water, gypsum, and additives.
- Forming and Pressing Area: This area houses the machinery where the gypsum slurry is spread onto paper and formed into sheets. Continuous conveyors, rollers, and cutting machines will be used to automate this process.
- Drying and Curing Section: This section will contain large kilns or ovens to dry the formed boards. The temperature and humidity in this area must be carefully controlled.
- Cutting and Packaging: Once the boards are fully dried and cured, they are cut into the required sizes and packaged for distribution.
- Quality Control Lab: A dedicated area for testing raw materials and finished products to ensure they meet required quality standards. This area will conduct tests such as moisture content, strength, fire resistance, and flexibility.
The layout should also include provisions for worker safety, equipment maintenance, and waste disposal. Sustainable practices, such as recycling scrap material and using energy-efficient equipment, should also be considered in the design.
Financial Projections and Investment
Capital Investment
The capital investment required for setting up a gypsum board manufacturing plant will include the following:
- Land Acquisition: The cost of purchasing or leasing land in an industrial zone or near a source of raw materials.
- Plant Construction: The cost of constructing the plant, including the establishment of all necessary infrastructure, utilities, and facilities.
- Machinery and Equipment: Investment in machinery such as crushers, mixers, continuous conveyors, kilns, cutting machines, and packaging systems.
- Raw Materials: Initial procurement of gypsum, paper, and other materials needed for the production process.
- Licensing and Permits: Fees related to obtaining the necessary licenses, safety certifications, and environmental permits.
Operating Costs
The primary operating costs for a gypsum board manufacturing plant include:
- Raw Material Costs: Ongoing expenses for purchasing gypsum, paper, and other necessary additives.
- Labor Costs: Wages for workers involved in production, quality control, maintenance, and administration.
- Energy Costs: Energy consumption for mixing, curing, and drying processes.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance and repair costs for machinery and equipment.
- Distribution and Logistics: The cost of packaging, warehousing, and transporting the finished boards to customers.
Revenue Projections
Revenue will primarily come from the sale of gypsum boards in different grades and specifications. The price of the boards can vary depending on the thickness, strength, and specific properties (e.g., fire-resistant, moisture-resistant). The plant can diversify its product offering to cater to different market segments, such as residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Gypsum board production has environmental and safety implications, and it is important to address these in the plant design and operations. Some key considerations include:
- Energy Use: The plant should implement energy-efficient equipment and explore renewable energy sources to reduce its carbon footprint.
- Water Use: Water conservation measures should be implemented, such as recycling water used in the mixing process.
- Waste Management: The plant should have a system in place to manage waste products, including scrap gypsum board and other byproducts, and aim to recycle or reuse as much waste as possible.
- Safety Standards: The plant must comply with local health and safety regulations, providing workers with personal protective equipment (PPE), ensuring proper ventilation in the working areas, and implementing fire and emergency safety protocols.
Regulatory Compliance
The plant will need to adhere to various regulations, including:
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with laws related to emissions, waste management, and water usage.
- Building Codes and Standards: Ensuring the gypsum boards produced meet industry standards for fire resistance, strength, and durability.
- Occupational Health and Safety: Adhering to local labor laws and safety regulations to protect workers in the manufacturing process.
FAQ
Q1: What is gypsum board used for?
Gypsum board is primarily used for interior walls and ceilings in buildings. It is a versatile material known for its fire resistance, sound insulation, and ease of installation.
Q2: How is gypsum board manufactured?
Gypsum board is manufactured by mixing gypsum powder with water and additives, then forming the mixture between two sheets of paper. The boards are then dried, cut to size, and packaged.
Q3: Is gypsum board fire-resistant?
Yes, gypsum board is fire-resistant due to the water content in the gypsum mineral. When exposed to heat, it releases water vapor, slowing down the spread of fire.
Q4: What is the market demand for gypsum board?
The demand for gypsum board is increasing due to rapid urbanization, growth in the construction industry, and the need for fire-resistant, energy-efficient building materials.
Q5: What are the environmental considerations in gypsum board production?
Environmental considerations include energy efficiency, water usage, waste management, and reducing the plant’s carbon footprint through sustainable practices.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-paints-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-personal-loan-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-plastic-packaging-market
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au