Medical staff must ensure appropriate patient positioning in prone surgical procedures because this practice prevents the development of pressure injuries and damage to nerves as well as respiratory difficulties. The prone head rest stands as an important element of safety which secures appropriate head and neck alignment for patients. A prone head rest works hand in hand with gel pads and OT table positioning gel pads to offer stability and distribute pressure during extended surgical operations. The correct procedure to employ a surgical prone head rest follows this sequential process.
Step 1: Assess Patient Positioning Needs
The surgical team needs to conduct an individual assessment of patient requirements which depend on the particular surgical procedure before installing the prone head rest. The selection of head rest and paste pads must factor in patients' head size along with neck flexibility and any existing medical considerations.
Step 2: Prepare the Operating Table
Operation table technicians need to adjust its height and tilt settings in order to match the requirements needed for patient positioning. OT table positioning gel pads function as protective padding which healthcare staff should place on the table to support pressure sore prevention.
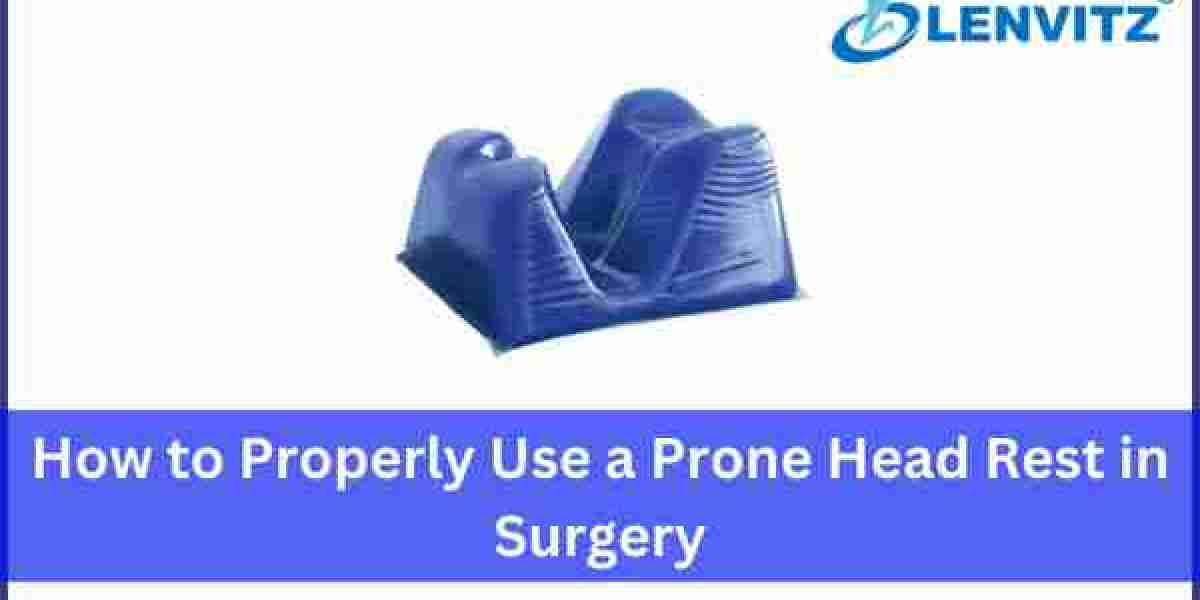
Step 3: Position the Prone Head Rest
The prone head rest must sit at the end of the operating table. The alignment of the device needs to match the patient’s shoulder area to provide proper neck and head stability. Prone head rest placement needs to remain stable while offering access for anesthesia administration to the patient’s airway.
Step 4: Use Gel Pads for Comfort and Safety
Proper patient comfort stems from placing gel pads strategically around the prone headrest to distribute pressure evenly. The pads facilitate pressure redistribution throughout the body structure which minimizes injuries to skin tissue as well as nerve damage. Stellungen pads should be positioned between the forehead and cheeks while avoiding direct face contact with the head rest for pressure injury prevention.
Step 5: Ensure Proper Airway Management
The maintenance of open ventilation remains one of the essential elements when performing prone positioning. Applied to the prone head rest must contain a ventilating area which enables breathing access yet maintains access for the anesthesia team. Medical staff should position the patient with their head in a manner that avoids restricting breathing by minimizing both flexed and extended positions.
Step 6: Secure the Patient’s Head
Secure the correctly positioned head by using additional support devices or straps when needed. Proper stability of the head throughout surgery prevents accidental movements which pose risks of misalignment and pressure injuries to the patient.
Step 7: Regular Monitoring During Surgery
The surgical team needs to check the patient's head position alongside monitoring their skin condition together with their breathing the entire time during the treatment. Timely readjustments will prevent complications from occurring.
Conclusion
The combination of a prone head rest and gel pads and OT table positioning gel pads delivers essential patient safety and comfort when performing surgeries in the prone position. Proper monitoring in addition to correct positioning techniques helps surgical teams to decrease procedural risks and create superior patient outcomes.