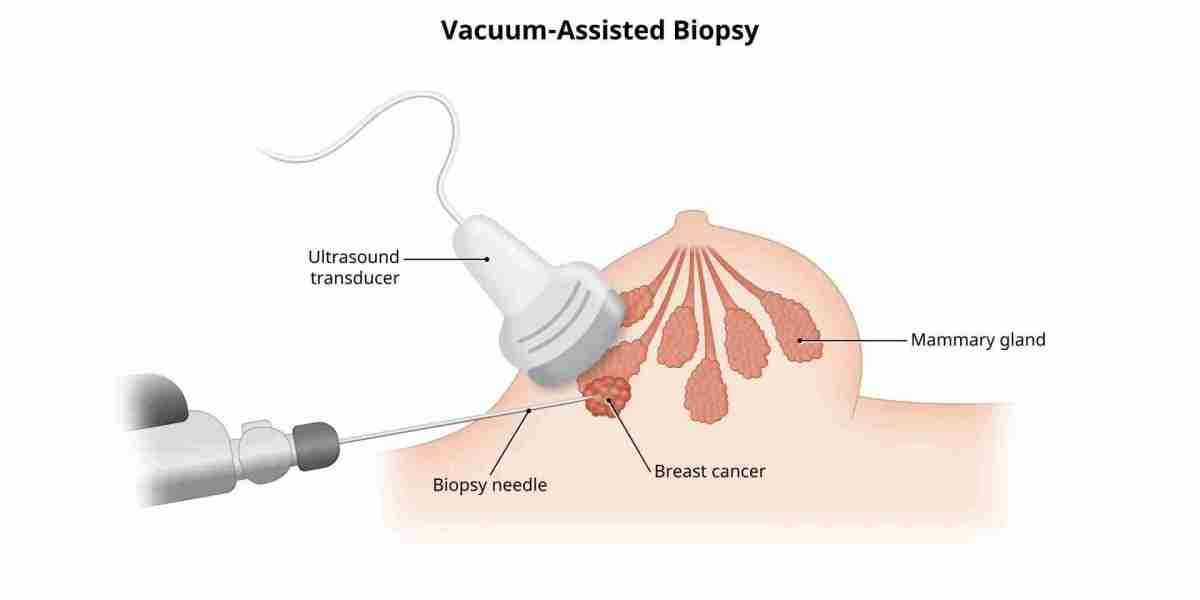
A biopsy is a medical procedure where a small sample of tissue is taken from the body for further examination. It is one of the most effective ways to diagnose various conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and even cancer. By analyzing tissue samples under a microscope, medical professionals can determine the presence of abnormalities and guide further treatment plans.
If you are scheduled for a Biopsy for diagnostic purposes(خزعة لأغراض التشخيص), it is natural to have concerns about the procedure, preparation, and what to expect. Proper preparation can help ease anxiety and ensure accurate results. This guide covers everything you need to know before undergoing a biopsy.
What is a Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes?
A Biopsy for diagnostic purposes involves removing a small amount of tissue or cells from a specific area of the body to be examined under a microscope. This procedure helps identify diseases, confirm a diagnosis, and determine the best course of treatment.
Why is a Biopsy Needed?
- Helps detect and diagnose conditions such as infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers.
- Confirms whether abnormal tissue growth is benign or malignant.
- Aids in developing an effective treatment plan based on accurate findings.
Types of Biopsies
There are several types of biopsies, each suited for different conditions and body areas:
- Needle Biopsy – A thin needle is used to extract tissue or fluid from an organ.
- Surgical Biopsy – Involves making a small incision to remove a larger tissue sample.
- Endoscopic Biopsy – Uses a flexible tube with a camera to collect tissue samples from internal organs.
- Skin Biopsy – Removes a sample of skin tissue for dermatological examinations.
How to Prepare for a Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes
Proper preparation can improve the accuracy of results and ensure a smooth procedure. Here are key steps to follow:
1. Discuss Medical History and Medications
- Inform the healthcare provider about any ongoing medical conditions.
- Provide a list of medications, including blood thinners, as they may need to be paused.
2. Follow Pre-Procedure Instructions
- Some biopsies require fasting for several hours before the procedure.
- Stay hydrated unless advised otherwise by the doctor.
3. Arrange for Transportation
- Depending on the type of biopsy, sedation or anesthesia may be used, affecting your ability to drive.
- Having someone accompany you can provide comfort and assistance.
4. Wear Comfortable Clothing
- Loose-fitting clothing is recommended for ease of access to the biopsy site.
- Avoid wearing jewelry or accessories that may interfere with the procedure.
What to Expect During the Biopsy Procedure
Understanding what happens during the procedure can help reduce anxiety and prepare you for the experience.
1. Local or General Anesthesia
- Some biopsies require local anesthesia to numb the area, while others may need general anesthesia for sedation.
- The choice of anesthesia depends on the location and complexity of the biopsy.
2. Tissue Sample Collection
- A small sample of tissue or fluid is removed using a needle, scalpel, or special instrument.
- The procedure typically takes between 15 to 60 minutes, depending on the type.
3. Minimal Discomfort
- Most biopsies cause only mild discomfort, similar to a pinprick or pressure sensation.
- Pain relief options may be provided if necessary.
Post-Biopsy Care and Recovery
Following a Biopsy for diagnostic purposes, proper aftercare is essential for healing and accurate results.
1. Monitor the Biopsy Site
- Mild swelling or bruising is normal and should subside within a few days.
- Keep the area clean and follow any dressing or bandage instructions.
2. Avoid Strenuous Activities
- Refrain from heavy lifting or intense physical activity for a few days.
- Follow specific guidelines based on the biopsy location.
3. Watch for Signs of Infection
- Redness, excessive swelling, or persistent pain should be reported to a healthcare provider.
- Fever or unusual discharge may indicate an infection requiring medical attention.
4. Wait for the Results
- Biopsy results usually take a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the analysis required.
- A follow-up appointment may be necessary to discuss the findings and next steps.
FAQs About Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes
1. Is a Biopsy Painful?
Most biopsies are performed under local anesthesia, minimizing discomfort. You may feel mild pressure or a brief pinch, but significant pain is uncommon.
2. How Long Does it Take to Recover from a Biopsy?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of biopsy. Most patients resume normal activities within a day or two, while more invasive biopsies may require a longer recovery period.
3. Are There Any Risks Associated with a Biopsy?
While generally safe, biopsies carry minimal risks such as mild bleeding, infection, or temporary soreness at the biopsy site. These risks are rare and manageable with proper aftercare.
4. How Accurate are Biopsy Results?
Biopsy results are highly accurate and provide critical information for diagnosing conditions. In some cases, additional testing may be required for confirmation.
Conclusion
A Biopsy for diagnostic purposes is a crucial medical procedure that helps detect and diagnose various health conditions. Understanding the process, preparing correctly, and following aftercare instructions can ensure a smooth experience. If you have any concerns, discussing them with a healthcare provider can provide reassurance and clarity.