Medical advancements have significantly improved disease diagnosis, with biopsies playing a crucial role in detecting and confirming various health conditions. Biopsy for diagnostic purposes(خزعة لأغراض التشخيص) is a widely used procedure that helps in identifying abnormalities in tissues or organs. By analyzing a small tissue sample, medical experts can determine the presence of diseases such as infections, inflammatory conditions, and even cancer. This article explores the science behind biopsies, their types, benefits, and what to expect during the procedure.
Why Are Biopsies Important?
- Accurate disease detection – Biopsies help in identifying diseases at an early stage, leading to timely treatment.
- Prevents misdiagnosis – Unlike imaging tests, biopsies provide a clear tissue analysis, reducing the chances of incorrect diagnoses.
- Helps in treatment planning – Understanding the exact nature of a disease allows for more effective treatment strategies.
Understanding the Biopsy Process
What is a Biopsy?
A biopsy is a medical procedure that involves extracting a small sample of tissue or cells from the body for examination under a microscope. Biopsy for diagnostic purposes is performed when other diagnostic tests, such as blood work or imaging, indicate potential abnormalities that require further investigation.
- Tissue sample analysis – The extracted sample is examined for cellular changes, infections, or cancerous growths.
- Performed on various body parts – Biopsies can be taken from the skin, muscles, organs, or bones, depending on the suspected condition.
- Guided by imaging techniques – Some biopsies use ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to ensure precision.
How Biopsies Help in Diagnosing Diseases
Biopsies provide a direct view of cellular structures, allowing experts to detect:
- Cancerous or precancerous changes – Confirms if a tumor is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
- Inflammatory conditions – Identifies autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammation.
- Infections and tissue damage – Detects bacterial, viral, or fungal infections affecting organs.
Different Types of Biopsy Procedures
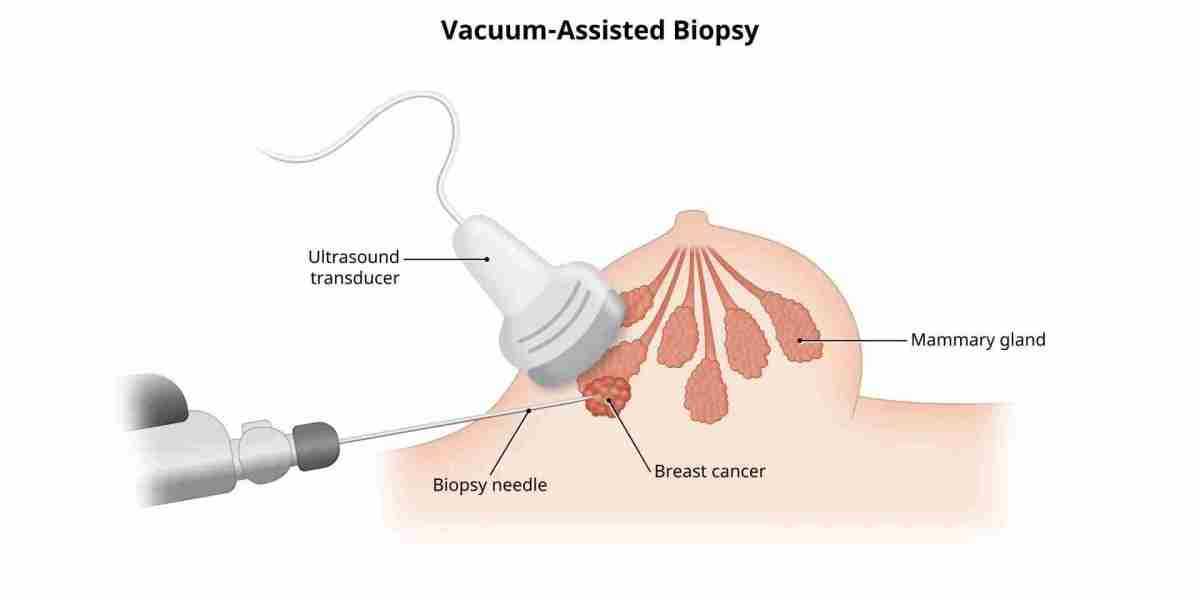
Needle Biopsy
A needle biopsy is one of the least invasive methods for obtaining a tissue sample. It is commonly used for organs like the liver, lungs, and thyroid.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) – Uses a thin needle to extract fluid or cells.
- Core Needle Biopsy (CNB) – Uses a thicker needle for a larger tissue sample, providing more detailed analysis.
- Image-guided biopsy – Uses ultrasound or CT scans to precisely target the affected area.
Excisional and Incisional Biopsy
These procedures involve surgical removal of tissue for examination.
- Excisional biopsy – Removes an entire lump or suspicious area, often used for skin and breast abnormalities.
- Incisional biopsy – Removes only a portion of the abnormal tissue, useful when a complete removal isn’t necessary.
Skin Biopsy
This method is used to diagnose skin conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and skin cancers.
- Punch biopsy – Uses a circular blade to remove a deep skin sample.
- Shave biopsy – Removes a thin layer of skin for superficial analysis.
- Excisional biopsy – Removes the entire lesion or abnormal skin growth.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
Bone marrow biopsies help in diagnosing blood disorders, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and anemia.
- Extracts bone marrow tissue – Taken from the hip bone using a specialized needle.
- Essential for blood-related conditions – Analyzes abnormal blood cell production.
- Helps in monitoring treatment response – Determines the effectiveness of chemotherapy or other blood disorder treatments.
What to Expect Before, During, and After a Biopsy
Pre-Biopsy Preparations
Before undergoing a biopsy, certain preparations are necessary to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Medical history review – Discussing medications, allergies, and underlying conditions.
- Fasting requirements – Some biopsies may require fasting before the procedure.
- Avoiding blood thinners – Reduces the risk of excessive bleeding.
The Biopsy Procedure
The process varies depending on the type of biopsy being performed, but generally follows these steps:
- Local or general anesthesia – To minimize discomfort, local anesthesia is used for minor biopsies, while major procedures may require general anesthesia.
- Tissue extraction – The sample is collected using a needle, scalpel, or special biopsy tool.
- Sample preservation – The tissue is preserved in a special solution before being sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Post-Biopsy Recovery and Care
After the biopsy, recovery depends on the type of procedure and the area from which the sample was taken.
- Mild discomfort or bruising – Common but temporary side effects.
- Avoiding strenuous activities – Helps in proper healing and reduces complications.
- Following up on results – Biopsy results are typically available within a few days to a week.
How Accurate Are Biopsy Results?
Reliability of Biopsy Analysis
Biopsy results are highly accurate when performed correctly, but certain factors can affect the precision of the diagnosis.
- Pathologist expertise – Experienced specialists analyze the sample to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
- Sample quality – A well-preserved and adequate tissue sample improves result reliability.
- Potential need for additional testing – Sometimes, further tests like molecular analysis may be required for a more detailed diagnosis.
Can a Biopsy Be Inconclusive?
In rare cases, a biopsy may not provide a definitive answer due to:
- Insufficient tissue sample – A new biopsy may be needed if the collected sample isn’t enough.
- Early-stage disease – Some conditions may not yet show significant cellular changes.
- Laboratory processing errors – Though rare, errors in sample handling can affect results.
The Future of Biopsy Technology
Advancements in Biopsy Techniques
Medical technology continues to improve biopsy procedures, making them less invasive and more precise.
- Liquid biopsy – A revolutionary method that detects cancer through a simple blood test.
- Robotic-assisted biopsies – Increases precision and minimizes risks.
- AI in pathology – Artificial intelligence enhances biopsy result analysis, reducing human error.
Benefits of Emerging Biopsy Innovations
New techniques improve patient experience by:
- Reducing discomfort – Less invasive procedures mean faster recovery.
- Providing faster results – Quicker turnaround times for diagnosis.
- Enhancing diagnostic accuracy – Advanced imaging and AI technology improve reliability.
Conclusion
Biopsy for diagnostic purposes is a vital tool in modern medicine, enabling accurate disease detection and treatment planning. With various biopsy types available, each tailored to specific conditions, this procedure plays a crucial role in diagnosing cancer, infections, and other medical disorders. As medical technology advances, biopsies are becoming more precise, less invasive, and more effective in ensuring accurate diagnoses. Understanding the process, benefits, and future innovations of biopsies helps individuals make informed decisions about their health.